Security Defaults feature is not new, but it is still unknown to many organizations. Mostly because it's not as visible as other features used to secure Azure Active Directory. If you are using Azure AD free, this feature might be super useful for you and can highly improve your organization's security with just a single switch.
Security defaults are available for free to all organizations.
What are Azure AD security defaults?
Azure AD security defaults improves protection against most common identity-related attacks. A single toggle (Security defaults feature is disabled by default) enables the following 5 security policies:
1. Requiring all users to register for Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication.
All users in the tenant (this setting cannot be scoped) must register for MFA within 14 days from the first logon after security default activation. After 14 days, users will not be able to log in until completing MFA registration.
2. Requiring administrators to do multifactor authentication.
Privileged access users will be required to pass the MFA challenge every time they log in. This policy applies to all users granted any of the following roles:
- Global administrator
- Application administrator
- Authentication administrator
- Billing administrator
- Cloud application administrator
- Conditional Access administrator
- Exchange administrator
- Helpdesk administrator
- Password administrator
- Privileged authentication administrator
- Security administrator
- SharePoint administrator
- User administrator
3. Blocking legacy authentication protocols.
Legacy authentications refer to:
- Clients that don't use modern authentication (for example, an Office 2010 client).
- Exchange Active Sync basic authentication
- Any client that uses older mail protocols such as IMAP, SMTP, or POP3.
Once security defaults are enabled, all authentication requests using legacy protocols will be blocked.
4. Requiring users to do multifactor authentication when necessary.
Azure AD will decide when it is necessary to prompt the user for MFA authentication. It takes into account factors like the user's location, a device that is being used to perform authentication, user's role and task. It applies to both – privileged accounts and regular user accounts.
5. Protecting privileged activities like access.
Azure services management services are protected as well. It means logging into Azure Portal, Azure PowerShell or Azure CLI will require an additional authentication method – MFA.
According to Microsoft's telemetry, more than 99.9% of account compromisation might be stopped by enabling any kind of Multi-Factor Authentication.
Authentication methods
In comparison to Conditional access, authentication methods available when using security defaults are limited only to
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Verification code from app or hardware token
If you would prefer to use text message or a call to phone, these methods are available only for Conditional access that requires an Azure AD P1 license.
How to enable security defaults?
To enable security defaults
- Sign in to Azure Portal using the account that has a Global Administrator, Security Administrator, or Conditional Access Administrator role.
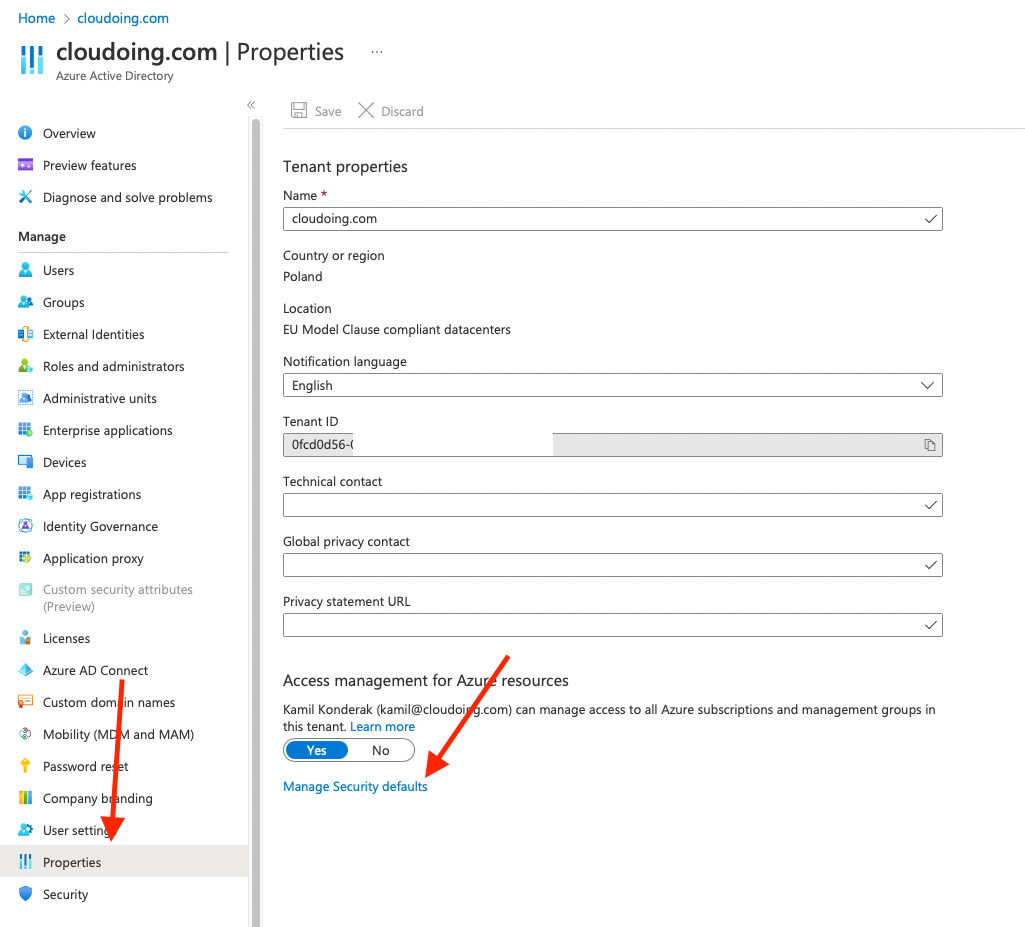
- Browse to Active Directory
- Go to Properties
- Select Manage Security defaults
5. Set Enable security defaults toggle to Yes.
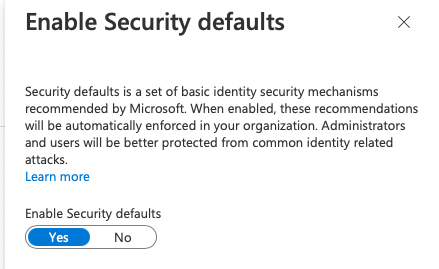
6. Save
Now you can enjoy more secure Azure AD and improved security score. 🥳




